What is Distributed Leadership? In short, It is a method of knowing leadership placement policy. It is primarily involved with the work of leadership, rather than specific leadership positions or responsibilities.
Table of Contents
What is Distributed Leadership?
So, what is Distributed Leadership? As we mentioned above, Distributed Leadership is a method to knowing how leadership takes place, especially among the people and the organisation. This method is conceptual and systematic. People and the organisation apply this to domains, including trade and even tourism.

However, it has advanced a lot and people used it in educational analysis. Yet, it doesn’t concentrate on aspects of the individual leader. Nor on the features of the situation. Instead, it foregrounds how participants involve in the tasks of an organisation.
Understanding distributed leadership means seeing leadership activities as an established and social process. Equally, at the intersection of leaders, followers, and situations.
Distributed leadership aims to enhance leadership potential. Especially within an organisation so that the organisation can develop and grow. They grow without any tricks or game-playing. It allows a company to become a more efficient. As a result, leaders within it pull in the same direction. And the same vision and values towards a standard set of goals to guide them.
In short, distributed leadership is giving leaders in company ownership by empowering them to lead their teams. And also to drive forward their strategies that provide towards the whole-company preferences.
Distributed Leadership vs Distributive Leadership
Distributed leadership and distributive leadership are two terms that may sound similar but actually refer to different concepts in the realm of leadership theory.
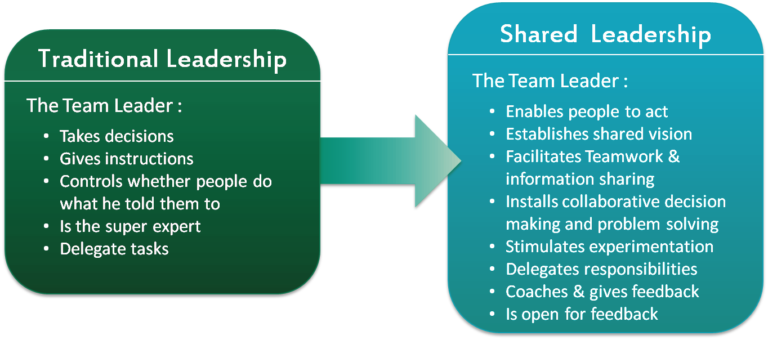
Distributed leadership emphasizes the idea of sharing leadership responsibilities and authority among multiple individuals or teams within an organization. This approach recognizes that effective leadership can come from various levels and areas of expertise within the organization, rather than being centralized in a single individual or hierarchical structure. In a distributed leadership model, decision-making and influence are dispersed throughout the organization, allowing for greater adaptability, innovation, and empowerment among team members.

On the other hand, distributive leadership refers to the equitable allocation or distribution of leadership roles, resources, and opportunities within a group or organization. This concept focuses on ensuring fairness and balance in how leadership responsibilities and benefits are distributed among members, with the aim of promoting collaboration, inclusivity, and collective ownership of goals and outcomes.
While both distributed leadership and distributive leadership involve the sharing or allocation of leadership functions, the former emphasizes the dispersion of leadership influence and decision-making throughout the organization, while the latter highlights the fair distribution of leadership roles and resources among group members.
Characteristics of Distributed Leadership
Distributed leadership is characterized by the delegation of authority and decision-making throughout an organization or team, rather than being concentrated solely in one leader. This approach encourages collaboration and teamwork, as well as the sharing of responsibilities among team members. It fosters a culture of trust and empowerment, where individuals are encouraged to contribute their unique skills and perspectives to achieve common goals. By distributing leadership, organizations can tap into the diverse talents of their members, leading to more effective problem-solving and innovation.
Key characteristics of distributed leadership include:
♦ Delegation of authority and decision-making
♦ Collaboration and teamwork
♦ Shared responsibilities
♦ Culture of trust and empowerment
♦ Utilization of diverse skills and perspectives
What were the Early Years of Distributed Leadership like?
Distributed leadership developed in the early 2000s. It evolved from theories like-
- Sociological
- Psychological
- Cognitive
- Anthropological theories.

Actually, distributed knowledge and activity theory is a result of Wenger’s communities of practice. First, it was an analytical and theoretical structure for school leadership. Back then, it would direct on how leadership was established in schools. And how it developed across the situational and social circumstances.
Much of the task is done in institutional research. And, they focused on the administrator mainly. Besides, reports were written of what was being done, but not how. Thus, it restricted transferability across contexts.
From this analysis, it was not clear how administrators reacted to the difficult circumstances in schools. Yet, some investigation on leadership has remained to focus on the role. Or the purpose of the assigned administrator. Such as
- Instructional leadership or
- Transformational leadership.
There has also been a notable shift to accepting leadership as a shared effort by more than one person.
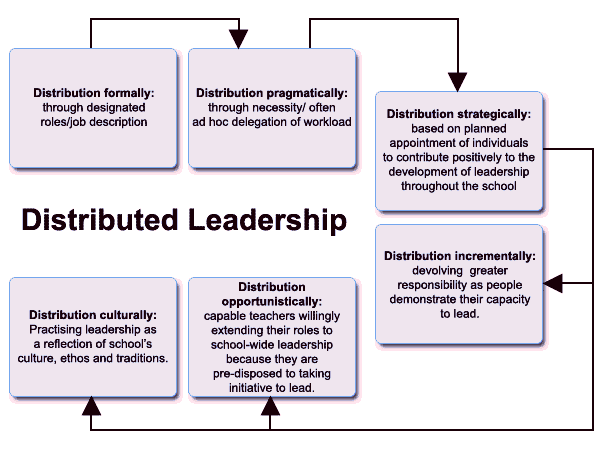
The current setup looks more broadly at several positions. It provides forms of leadership throughout the school. Including
- Democratic leadership
- Teacher leadership
- Shared leadership
- Collaborative leadership
Distributed leadership draws on these multi-agent aspects. For example, to explain how performers work to secure the conditions. Especially for advancing teaching and learning in schools.
In other words, distributed leadership is not an action, instead of a method.
What are the Benefits of Distributed Leadership?

It is impossible for one person to have the necessary knowledge, time and skills to manage every phase of the organisation. Especially as an organisation becomes more complex. Thus, distributing leadership throughout the organisation may:
- Boost employee commitment and engagement. Due to understanding of collective liability for the organisation’s progress
- Promote co-operative ideas and help produce new solutions to old obstacles
- Support more efficient and conscious decision-making
- Assist in developing a higher sense of openness and belief in the organisation
- Help succession planning outlining. So that it can help organisations to recognise and sustain leadership potential.
- Inspire more high-grade teamwork at all levels of the organisation
- Give people a more resilient and versatile approach to work
- Enhance knowledge-sharing and learning. It can be inside and beyond departments as different groups of people work together.
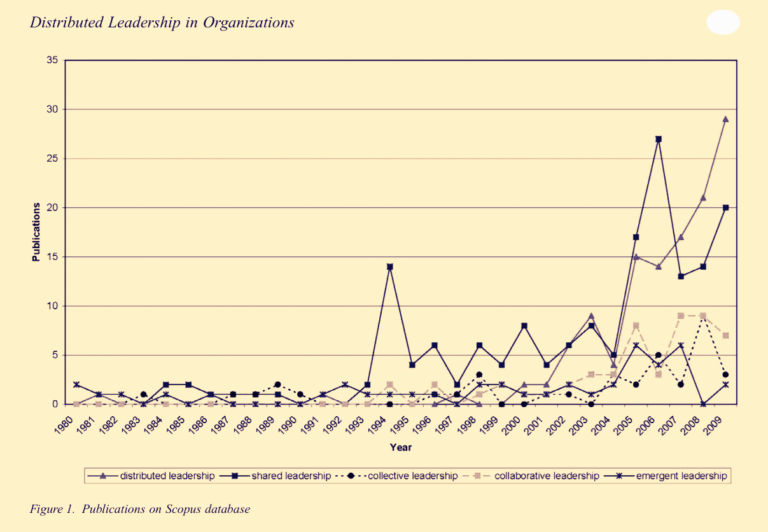
Source: Scopus database
What is the Theory of Distributed Leadership?
Only knowing what is distributed leadership is not enough. To fully understand, one must know its theory as well.
Leadership is often considered as something that is acted out or done by an individual to influence others. Social or shared leadership often still sees leadership as activities done by individuals. Yet, with the cooperation with others. Taking a distributed perspective, leadership is a rising resource of the system. It sits between-
- who consider leadership as a result of personal agency and
- who view it as a consequence of the circumstances.
Activity Theory of Distributed Leadership
Activity theory is a comprehensive social science strategy. Thus, it helps us to understand individual behaviour as contextualised in a circumstance. This established viewpoint increases the unit of analysis to the collective rather than individual, and analyses the connection between actions.
Although this proposal aims to learn the individual, the unit of analysis is the more extensive system. For instance, in which that individual participates.
Engestrom recognises three ages of activity theory and associated researcher:
- First-generation (1978). A model concentrated on the individual (subject-object-mediating artefact) by Lev Vygotsky.
- Second generation (1981). The extension of the model to add collective action, by Alexei Leont’ev.
- Third generation (1987). A networked knowledge of interactive activity systems, proposed by Engestrom himself.
Barbara Rogoff, another Activity Theory scholar, develops this work in two ways:
- First- foregrounding of the individual. Dropping sight of the relationship of the system is not acceptable.
- Second- there are three different levels of resolutions-
1. Interpersonal level
2. Cultural/community and
3. Institutional/cultural planes
These are required to read the different level’s activity. An assigned leader takes this networked and multi-level approach to give “Context of Action”. And manage the stress between agency and distribution.
Spillane and Gronn both bring on the use of activity theory in the field of a leadership analysis. As a result, it spread out of Mintzberg’s studies of work activity. Besides witnessing managers through structured observations to document what they do. The nature of this documentation was innovative and exciting.
However, it was eventually considered shallow. As it did not distinguish between managerial and non-managerial tasks. There were still unsettled questions. Questions about how management acted, and it did not show leadership effectiveness.
What is Distributed Leadership Viewpoint?
Now you may be wondering what Distributed Leadership viewpoint is? Well, in brief, it is to look at leadership activity as a situated and social process. As well as drawing on distributed cognition and activity theory.

Distributed Cognition lies at the intersection of sociology, psychology, and cognitive science. Thus, it is the theory that is spread across the situation, tools, context, and other people. It was introduced with the work of anthropologist Edwin Hutchins in the 1990s. With his navigation on a naval aircraft carrier studies.
His work on learning established cognition. He pointed to the resolution that cognition is distributed socially. Rather than looking for knowledge structures within an individual. His work showed us that cognitive activity or knowing what to do was a fixed method influenced by- tools, situations and other people.
What is Distributed Leadership Theory in Education?
Distributed leadership theory in education suggests that leadership responsibilities are shared among various individuals rather than being centralized with one person. This approach empowers teachers, staff, and even students to take on leadership roles, contributing to decision-making and school improvement.
♦ Empowers teachers, staff, and students
♦ Shares leadership responsibilities
♦ Contributes to decision-making and school improvement
Final Thought
We hope you have the overall idea about ‘what is distributed leadership’. In order to run big companies, distributed leadership is very helpful. Distributed leadership helps establish a hierarchy in a workplace, which in turn helps to do work systematically and efficiently. To refine your leadership skills and learn more about distributed leadership take our Certificate in Leadership Course.
FAQs
1. Are distributed leadership and distributive leadership same?
No, distributed leadership and distributive leadership are not the same. Distributed leadership refers to a leadership approach where responsibility and decision-making are shared among a group of individuals within an organization, promoting collaboration and shared accountability. Distributive leadership, on the other hand, refers to the allocation of leadership tasks or responsibilities across different individuals or groups within an organization.
2. What are the examples of distributed leadership in schools?
In schools, distributed leadership includes teachers leading committees, student councils, professional learning groups, mentoring programs, and shared decision-making among staff.
3. What are the advantages of distributed leadership?
Distributed leadership promotes collaboration and innovation within teams, increases employee engagement and ownership, fosters diverse perspectives, and enhances decision-making efficiency.
Recent posts
- When Should You Start Writing Your College Essay? A Strategic Timeline for Success
- 12 Easy Ways to Learn Even and Odd Numbers
- Top 5 Study Tools for College Students
- 11 Essential Tools Every Online Learner Needs in 2024
- How to Leverage the Global Talent Visa for Advancing Your Education
- From Study Notes to Assignments: 15 Ways PDF Editors Boost Academic Productivity
- How Blockchain is Transforming Education | 2024 Insights
- 5 Tips for Starting Your Cyber Security Analyst Career
- The Evolution of Online Assignment Help Services in the UK: Trends and Benefits
- Effective Time Management Strategies for Managing Online College Coursework






 August 12, 2023
August 12, 2023








