The days of eating farm-fresh foods regularly are difference between use by and best Best Before dates. In our day to day busy life, we do not get enough time to buy fresh groceries or make our own food, so we buy our weekly or monthly rations together. Despite all, we want us and our family to eat healthy and good food.
Thanks to food manufacturers and the grocery shops, who process and package all the grains, raw vegetables, meats, canned foods, and ready-to-go foods with labels. The label shows the quantity of the food, nutritional values, and dates like manufacturing dates, selling dates, and use by and best before dates. These dates sometimes leave us all confused while buying the food.
There are two kinds of dates on the foods label that we should always keep an eye on Use By dates and Best Before dates. The dates ensure that if the food is okay to eat or not.
These dates are one of the key factors in maintaining food hygiene.
Table of Contents
What is Use By Dates & Best Before Dates?
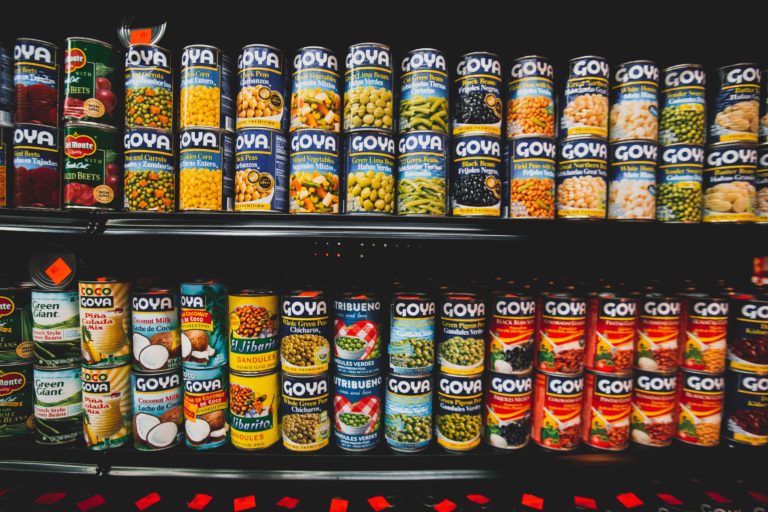

Grocery shops and food manufacturers label each food package mainly with two dates: the manufacturing date or when the food was processed or picked. The other date is the expiration date, the date from which the food may become inedible.
Date marks show how long food can be preserved until it starts to deteriorate or becomes unhealthy to eat. Use by dates and best before dates are the two types of date markings. The food supplier is responsible to correctly label food with a use by or best before dates.
Use By Dates
Use-by dates on foods indicate that the particular food will become inedible or unsafe to eat after that specific date. It will get rotten or may become infected with harmful germs. This kind of food should be eaten before the given date, and it is also illegal to sell the food after the use-by date is over.
Use by dates is usually stamped on easily perishable foods like meats, dairy products and ready to eat meals. These foods should be kept frozen until you are prepared to eat.
Best Before Dates
Best before dates shows the time till which the food is best to eat; after that time, the food will remain edible, but it may lose its taste, colour or textures. These foods can be consumed for a while after the best before date is over. The food can be legally sold after the best before dates.
Foods like bread, biscuits, canned foods and vegetables and fruits, grains and dry pasta come with the best be fore dates.
Suppliers must put on any instruction that is required to store the food properly if there is a chance the food may get spoilt even before use by or best before dates—for example, refrigerating or freezing.
What is the Difference between Use By & Best Before Dates?

Use By Dates
- 1. Use by date is given for safety.
- 2. Use By Dates gives a time limit before which the food should be eaten.
- 3. After the use-by date, the food should be disposed of, even if it looks or smells alright.
- 4. It is necessary to check on the date; eating foods after the dates may cause food poisoning. So do not eat, cook or freeze food after its use-by date is over.
- 5. Foods like meats, fish, pre-processed food and dairy products are labelled with use-by dates.
- 6. Freezing the foods like meats closely before the use-by dates are over can increase the time they can be kept good, but once they are defrosted, they should be eaten within 24 hours.
Best Before Dates
- 1. The best before date is about quality.
- 2.Foods taste and quality remain intact before the best before dates.
- 3. Foods can still be consumed after the date is over, but their colour, texture and taste changes.
- 4. Best before dates appears on foods like frozen foods, dried foods, tinned foods etc.
- 5. The best before date is only accurate if the food is kept stored according to the instructions on the package.
- 6. Once the packaging is torn and the food comes into contact with air, the best before date may not work as contamination may start taking place.
Who and When it is Decided Foods Need to be Labelled by Use-by or Best-before Dates?

When applying a label to a food product, the food business operator (usually the manufacturer or producer) is responsible for determining whether a ‘best before or use by date’ is needed for shelf-life declaration.
When a food manufacturer or supplier is designing their food safety management system, they can evaluate if food needs a ‘best before or use-by date’. The process by which food manufacturers decide how they declare the dates must be documented to ensure trust and quality.
Does All Food Need Use by or Best Before Date?
All food doesn’t require a use-by or best before dates. These foods are:
- Fresh fruit and vegetables, which have not been peeled, cut or similarly treated.
- Different kind of wines and beverages falling within CN code 2206 00 obtained from grapes.
- Beverages with 10 % or more by volume of alcohol
- Baked or pastry cooked foods that should be consumed within 24 hours of its making.
- Cooking Salt
- Vinegar
- Solid sugar
- Sweet products which are entirely made of flavoured and coloured sugar.
Food Safety Practices

Every food business must check that all foods they receive and store have proper use by or best previous dates. It is necessary to handle food maintaining hygiene, and check that the food is used within the appropriate time frame.
Food should be stored in the market using the First In, First Out (FIFO) process. These are the practices that fall under this process:
- 1. Make sure the food products that are received first are first to be sold.
- 2. Move the foods in front of the shelf, which is nearing their use by or best before dates.
- 3. If foods are not stored in their original packaging, ensure that they are correctly labelled and dated.
- 4. Frequently check the best before and use by dates of the food.
- 5. If any foods show signs of spoilage, discard them.
Maintaining Food Hygiene
It is mandatory to maintain food safety and hygiene standards during food preparation, production and consumption. From the farmer who grows the food to consumers who bought the food from the store, the entire food chain is hampered if proper hygiene is not followed. Contamination and spoiling of food pose a significant health risk in recent days and lead to major food wastage.

Here are a few rules to maintain food hygiene:
- 1. Thoroughly clean and disinfect kitchen surfaces, chopping boards, utensils and cutleries before starting to prepare food on them.
- 2. Wash dishes, utensils and knives that came in contact with raw fish and meats.
- 3. Use different utensils to process raw foods and ready to eat foods.
- 4. Wash hands before preparing food and handling raw foods.
- 5. Keep raw food and ready to eat food separate from each other all the time.
- 6. Keep the raw foods below and ready to eat food above while storing foods in the freezer. If possible, do not keep the raw food and ready to eat food in the same place.
- 7. Use completely different utensils and sponge to clean ready to eat foods.
To know more about food hygiene, check out the Food Hygiene Certificate course!
Conclusion
To live a healthy life, we need to eat good and safe foods. It is always essential to check what we are eating and if it is safe to eat. Next time you go grocery shopping, please do check the dates.
Further resource
- Essential Things to Know about Reheating Food in the Oven
- What Foods Can You Freeze? A Complete Guide on Freezing Food
- Healthy Food List: Top 50 Weight-Loss Friendly Foods
- 20 Healthy Foods to Eat Everyday According to Expert Advice
- Is Baking a Good career? 15 Reasons To Be A Professional Baker
- Chef Hierarchy: What are the Types of Chefs?






 August 10, 2023
August 10, 2023








