Are you an employee working in an office or other premises? Do you know what rights you have as an employee? Read this blog to learn about the 10 Rights of Employees in the Workplace.
If you are a worker, you spend a large portion of your valuable time at work every day. While working for employers, you are entitled to many benefits, according to UK employment law. Employment law ensures workers fair pay and other benefits in the workplace.
Employment law covers all rights and obligations in the employer-employee relationship. It ensures that your employer treats you fairly in the workplace. And it’ll make you aware that your employers are following all regulations regarding employment and anti-discrimination laws.
Maybe you don’t know that you are entitled to certain rights at work. But, having the knowledge of the rights allows you to have certain benefits in the workplace. Read this blog to learn every right you are entitled to at the workplace according to UK employment law.
Table of Contents
What are Employee Rights?
All the employees have certain rights in their workplace. A right is the ability to legally engage in any behaviour that is protected by the law or social sanction. And employee rights refer to the moral or legal entitlement to ensure fair treatment of employees at work. Allyship is one of the main drivers of inclusion in the workplace. Allyship training prepares employees to better support, collaborate with and advocate for people from minority and marginalized groups. In other words, it’s the right that an employee has to be treated in a fair, morally acceptable, or legal way when a company employs them. Employee rights include both legal rights and human rights.

Your rights as an employee may vary depending on your employment status. The main types of employment status in the UK are:
It is important to note that all employees are workers. But all workers are not employees. That’s why an employee has all the rights a worker has with some other rights and responsibilities.
However, you may have a different employment status in tax law. In employment law, your employment status will determine:
You can read more about employment laws in the UK below.
What Are Your Legal Rights as an Employee?
If you’re wondering, what are the basic employment rights for an employee, we have the answer for you. As per the UK Government, you are entitled to certain employment rights, such as
10 Rights of Employees in the Workplace
Employment law covers all the rights and obligations within the employer-employee relationship. The employment law includes not only current employees but also former employees and job applicants. There are so many employment rights you are entitled to; you might be aware of them.

We put together a list of 10 rights of employees in the workplace you should know about. Read on to know more about UK employment law!
1. Your right as a job applicant
2. Employment contract
3. Wage equality
4 No discrimination in the workplace
5. No sexual harassment in the workplace
6. Safe workplace environment
7. Medical and family leave
8. Fixed-term and part-time right
9. Rest breaks and reasonable working hours
10. You have the right to stand up for yourself.
1. Your Right as a Job Applicant
Do you know that you have employment rights even if you are not an employee of this organisation? You have a certain right before starting to work there. During the recruitment process, you have the right to be free from discrimination.
That means the potential employer has no right to discriminate against you based on age, gender, race, national origin or religion. For example, a prospective employer cannot ask you a certain family-related question during an interview.
2. Employment Contract
 Employers do not always give employees contracts of employment when starting to work. However, they are not legally obligated to provide you with a contract when joining. Although, you should receive a written statement within the first two months. The basic details and the main terms and conditions of their employment should be clearly stated in the contract.
Employers do not always give employees contracts of employment when starting to work. However, they are not legally obligated to provide you with a contract when joining. Although, you should receive a written statement within the first two months. The basic details and the main terms and conditions of their employment should be clearly stated in the contract.
The contract should include the following:
- Job title,
- Expected working hours,
- Monthly salary,
- Paid holiday and sick leave entitlement,
- Details of any applicable pension scheme,
- The minimum notice period,
- Disciplinary process,
- And the procedure for reporting a grievance.
3. Wage Equality
Employers are not required to pay the same salary to all employees. But according to NMW, employers should pay the same wages to the employees who perform similar tasks and have the same skillset. And the workplace environments should also be similar in circumstance.
Employees who worked more than 8 hours per day or 40 hours per week are entitled to overtime pay. The employer has to pay a time-and-a-half rate of pay for employees who work additional hours. However, salaried employees are not eligible for their overtime work.
4. No Discrimination in the Workplace
Employers or HR can not discriminate against employees in the workplace. This applies to all forms of discrimination, including:
- Gender
- Pregnancy
- Religion
- Race, ethnicity or national origin
- Age
- Disability
- Immigrant Status.
5. No Sexual Harassment in the Workplace

Any kind of sexual harassment in the workplace is illegal and may result in prosecution. The UK labour law protects employees against this in the workplace.
It is sexual harassment if you are forced to participate in sexual favours for job security or receive a promotion. Additionally, being subjected to extremely pervasive comments in the workplace is also sexual harassment.
6. Safe Workplace Environment
The workplace environment should be safe and has no health and safety hazards. So, the employer should make their workplace safe and free from any potential hazard for their employees.
According to the Health and safety laws, employers have a statutory duty to take care of their employee’s health and safety in the workplace. The employer should provide a clean environment for working by providing employees with:
- First aid equipment,
- Protective clothing (such as PPE when needed),
- Drinking water and washing facilities,
- And ensure all the machinery is safe to use.
If an employer fails to provide a safe working environment, you can file a complaint with the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). It is one of the best ways to bring hazardous situations in a non-threatening manner in front of authorities and employers.
7. Medical and Family Leave
According to the labour law, employees can take leaves from work after a certain period of working with the organisation. An employee must have worked for a year or at least 1,250 hours for the same employer. And also the employer also has 50 or more employees. You can take time off for:
- Caring for an extremely ill family member.
- Birth of a baby.
- Adopting a child.
- Recovering from an illness you have etc.

UK labour law allows an employee to have 12 weeks of unpaid leave while their job is secure. Female employees can take time off for antenatal care and can take 52 weeks of statutory maternity leave. Male employees can take 1-2 weeks of paternity leave when the baby is due or born.
If you are adopting a child, you are entitled to 6 months paid leave and 6 months unpaid leave. However, if your partner works in the same company, he/she is entitled to paternity leave.
If an employee is pregnant or on maternity leave and receives a dismissal notice, this notice must contain a written explanation of the reason.
You have the right to submit a request for flexible working hours after 26 weeks of working for an employer. But you can only make one request to work flexibly per year.
8. Fixed-Term and Part-Time Employee Rights
Employees working in the same role should have the same contract rights whether they are permanent or part-time. However, entitlements to holidays and similar rights for part-time workers may be calculated on a pro-rata basis.
The working hours of part-time and permanent workers would vary from one company to another. Thus, it is impossible to calculate specific working hours that distinguish a part-time worker from a full-time worker.
9. Rest Breaks and Reasonable Working Hours

Health and safety laws state that employees have a right to daily and weekly rest breaks. If the working day exceeds 6 hours, employees are entitled to have a 20 minutes rest period to eat or hydrate. Employees are also entitled to at least one full day-off of every seven days.
Also, your employer cannot force you to work more than 48 hours a week. If they ask for it, there should be additional pay and there should be a contract stating the terms.
10. You Have the Right to Stand up for Yourself
If you feel your rights are being violated in the workplace, you have the right to be free to stand up for yourself. You can respectfully express yourself to the employer about the injustice.
When employees file a claim against their employer for violating one of their rights, there should be no employer retaliation. The rights of being free from retaliation are also known as “whistle-blower” rights.
If you feel that there would be a punishment or retaliation, you can talk to other agencies. Agencies like OSHA and other government entities are perfect for standing up for employees who are experiencing any type of violation of rights in the workplace.
What is Employment Law?
To put it simply, employment law is legislation that regulates the employer-employee relationship. It describes how an employer and employee must behave in a working environment. It also explains what employers can expect from you as an employee or what your employers can ask you to do. And more importantly, what are your rights as employees at work.
You might be thinking about why you’re reading about employment law. Employment law ensures that the rights of employees are met. They are designed to ensure fairness at work and help boost productivity and respond to demographic and social change. In addition, the legislation makes a positive contribution to employee relationships. It also increases employees’ sense of fairness and trust in their employer.
Let’s take a look at what to what extent employment law covers rights of employees in the workplace.

Employment Law in Protecting Rights of Employees
The employment laws cover a wide range of issues relating to the work environment and processes. The following are some examples of what’s covered by employment law—including:
- Equal pay
- Age discrimination
- Bullying and harassment
- Parental leave
- Disability
- Employment contracts
- Dismissal
- Employee grievances
- Holiday pay
- Minimum wage
- Discrimination based on gender, race, religion, or sexuality
- Redundancy
- Working hours.
Employment law aims to protect employees and employers. In addition, it makes sure you are fairly paid by your employers. Also, it protects children from child labour. It improves and regulates relationships and interactions between employer and employee.
The employment laws protect workers suffering from unfavourable treatment in the workplace. Without these laws and regulations, workers can’t improve their situation. Thus, employment laws are extremely important for UK employees.
What are the Laws that Protect the Rights of Employees?
The UK authorities have enacted laws to ensure the rights of employees are met. In addition, they make sure that you are aware of your rights and your responsibilities towards employers.
In the UK, multiple laws outline and protect worker’s rights and employee’s rights. However, these laws can be quite complex for employees and employers to understand. We have put together a list of employment laws in the UK that are most relevant and helpful.

Employment laws are essential to every business. Failing to adhere to these laws may lead an employer to face an employment tribunal. Below are some essential employment laws and legislations.
Employment Rights Act, 1996
This Employment Rights Act is one of the most inclusive pieces of employment law legislation. Also, it is an update to older labour law. Employment Rights Act covers a wide range of topics, such as employment contracts, redundancy, family-friendly leave, and unfair dismissal.
National Minimum Wage Act 1998
This legislation set out the National Minimum Wage for employees and workers across the UK. The government regularly reviews this law to keep the National Minimum Wage in line with inflation. Thus, the minimum wage can change at any time. As an employer or employee, it’s vital for you to be aware of any updates to National Minimum Wage.
Employment Relations Act 1999
This Employment Relations Act establishes a number of rights at work for:
- Trade union recognition,
- Derecognition,
- And industrial actions.
The Maternity and Parental Leave etc. Regulations 1999
UK labour statutory legislation governs employees’ rights for time off from work for maternity or paternity leave.
As per the Maternity and Parental Leave etc. Regulations, a female employee is entitled to 18 weeks of ordinary maternity leave. And an additional leave of 29 weeks if she’s been working for the company for more than one year. The ordinary leave will be paid whereas the additional leave will be unpaid.
Part-Time Workers (Prevention of Less Favourable Treatment) Regulations 2000
This UK labour law requires employers to provide employees on part-time contracts with equal treatment to the full-time staff who do the same jobs.
Agency Workers Regulations 2010
This Agency Workers legislation aims to prevent discrimination against any agency workers. For example, employers pay the correct amount, give them the right amount of holiday days, and safe working conditions as per this law.
The Equality Act 2010
The Equality Act prevents discrimination in the workplace and also in the recruitment process. It makes the law easier to understand and helps to strengthen the protection on some occasions. It determines the different ways in which it’s illegal to treat an employee.
Transfer of Undertakings (Protection of Employment) Regulations 2006
The purpose of the Transfer of Undertaking (Protection of Employment) or TUPE regulations is to ensure employee rights during a business transfer. The process of this regulation is very complex. However, it ensures that staffs receive fair treatment from their new employer.
You will find all the relevant, up to date and newly enacted legislation about the rights of employees for the UK, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland in Legislation.gov.uk.
Frequently Asked Questions
About Rights of Employees in the Workplace
Information is power. If you’re not well-informed, you might not even recognise if you’re being discriminated or mistreated in the workplace. So, read more about some of the most asked questions regarding the rights of employees in the workplace. Here you’ll find answers to the following questions.
- Who Protects Employees Rights?
- What Are My Rights as a Disabled Employee?
- What are My Statutory Rights as an Employee?
- Do Agency Workers have the Same Rights as Employees?
- What Rights does a Temporary Employee Have?
- Do Employees on Probation have Rights?
- What are Employee Privacy Rights?
- What Are My Rights as a Pregnant Employee?
- What Are My Rights as an Employee with Mental Illness?
- What Are My Rights as an Employee Without a Contract?
Find the answers to these questions below.
1. Who Protects Employees Rights?
In the UK, the rights of employees are protected by the laws and regulations put in place by the government. You can read more about the laws in the list of ‘Laws that Protect the Rights of Employees’ section.
If you’re not receiving National Minimum Wage or National Living Wage, or if there are any violations of the rights of employees, you may try to resolve them informally. Or you can do the following –
2. What Are My Rights as a Disabled Employee?
Have you ever wondered, ‘what are my rights as an employee with a disability?’
Know that it’s illegal for an employer to discriminate against anyone because of a disability. And the Equality Act, 2010 protects your rights as an employee with a disability.
Even during the recruitment process, the recruitment panel can only make limited enquiries about your health or disability. Also, your employer has to make reasonable adjustments to make sure you aren’t at a disadvantage compared to other employees in the workplace. For instance, providing flexible working hours or giving a special piece of equipment to help you do the job. Also, you can’t be chosen for redundancy or forced to retire if you become disabled.
You can find more about disability rights here.
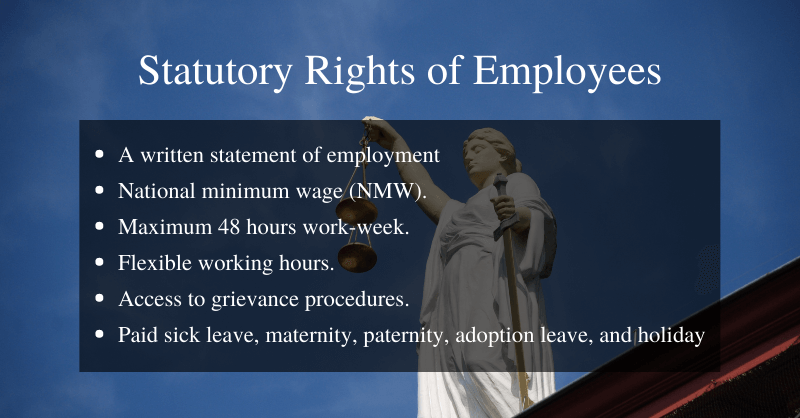
3. What are My Statutory Rights as an Employee?
Statutory rights are the employment rights that can’t be overridden by any contractual agreement, such as your employment contract. They are granted to you by the government. And statutory rights automatically apply to all employers and employees. Besides, statutory rights are intended to provide legal protection to both employers and employees. – mentioned by Mark Wenger, founder of Mygov.me
Some statutory rights of employees are –
- A written statement of employment within 2 months of starting work.
- Getting paid the national minimum wage (NMW).
- Paid sick leave, maternity, paternity, adoption leave, and holiday.
- A maximum of 48 hours work-week.
- Applying for flexible working hours.
- Having access to grievance procedures.
You can find more information on – Statutory Sick Pay, Statutory Maternity Pay, Statutory Paternity Pay and Statutory Adoption Pay.
4. Do Agency Workers have the Same Rights as Employees?
Agency workers have a contract with an agency, but they work for a hirer temporarily. And agencies can be recruitment agencies, such as temp agencies or entertainment and modelling agencies.
As an agency worker, you have the same rights as any other employees and workers. For instance, getting the National Minimum Wage or National Living Wage, no illegal deductions, receiving payment on time with payslips etc.
For more information, you can check your employment rights as an agency worker.
5. What Rights does a Temporary Employee Have?
If you’re thinking, “do I have rights as a temporary employee?” Yes, you do.
As a temporary employee, you have the right to basic employment and working conditions.
Also, you are entitled to the same legal protections as any other worker. You have a right to fair wages and overtime pay, receive protection against discrimination, harassment, and wrongful termination.
6. Do Employees on Probation have Rights?
Do you have any rights while on probation at work? Yes, while there is no fixed trial period for probation, your employer is expected to be reasonable.
Probationary periods allow the employee to assess whether it’s a right fit for employees. But even then, employees have statutory employment rights. Some of those rights include unlawful discrimination, National Minimum Wage, working time directive, maternity and paternity leave, statutory sick pay, and time off for dependents.
7. What are Employee Privacy Rights?
Many employers monitor their employees in various ways, such as using CCTV, drug testing, bag searches, checking emails or web history.
Any kind of monitoring involving taking data, images, or drug testing are protected by Data protection law. You can also check the staff handbook or employment contract to know your privacy rights at work.
Do Employers Have the Right to Drug Test Employees? In general, employers must have consent for a drug test. And employees can’t be forced to take a drugs test. But if the employer has good grounds for testing, and they refuse to take the test, they may face disciplinary action.
However, if a search or drug test is badly handled by the employer, you might be able to make a claim for discrimination, assault or false imprisonment.
8. What Are My Rights as a Pregnant Employee?
UK government allows pregnant employees 4 main legal rights. They are –
Related:
1. How to Become an HR Professional: A Career Guide
2. Employability Skills: A Guide to Skills Employers Look For
3. 8 Administrative Office Skills: Employers Are Looking For
4. How to Set SMART Goals to advance your Career

1. Paid time off for antenatal/prenatal care
This time off may be for medical appointments, antenatal, or parenting classes.
2. Maternity leave
The statutory maternity leave is 52 weeks. But you may choose not to take 52 weeks off.
However, you have to take 2 weeks’ leave after your baby is born. If you work in a factory, you have to be on leave for 4 weeks.
3. Maternity pay or maternity allowance
You have the right to statutory maternity pay (SMP). It is paid for up to 39 weeks.
For the first 6 weeks, 90% of average weekly earnings (before tax)
For the next 33 weeks, £151.97 or 90% of your average weekly earnings (whichever is lower)
4. Protection against unfair treatment, discrimination, or dismissal
Also, employers must ensure the health and safety of pregnant employees. For instance, no heavy lifting or carrying, no long hours, and no working without adequate breaks. And lastly, it’s against the law to discriminate against anyone because of being pregnant.
9. What Are My Rights as an Employee with Mental Illness?
Mental Health Foundation reported that almost 15% of employees in the UK are affected by mental health issues. Some common ones are depression, anxiety, stress. But they could be more severe, such as bipolar or PTSD.
Regardless of the nature of the mental illness, employers have a ‘duty of care’. That means your employer must do everything they can to support your employees’ health, safety, and wellbeing. An employer must ensure a safe, supporting working environment, protect staff from discrimination and carry out risk assessments to make sure they’re safe.
10. What Are My Rights as an Employee Without a Contract?
Even without a written contract, an employee can legally work for an employer. In such a case, the employment relationship is based on a verbal employment contract. And your terms of employment might be expressed, implied or subject to statutory rights. However, without a contract of employment, you will be officially classed as a worker instead of an employee.
So even if you’re an employee without a contract, you have the same statutory rights as others.
Conclusion
UK employment law covers all rights and obligations in the employer-employee relationship. It is very important for an employee to be treated fairly in the workplace by their employer. It allows employees to have a positive and enriching environment that promotes career development and productive work. So, UK employment laws are important to know your employee rights at work. Also, having the knowledge of the rights will enable you to have certain benefits in the workplace.
Know the rights of employees. Be Prepared and Safe!
Not satisfied with the above information? Want to know more about UK employment law? We, One Education, provide an online course on UK employment law. Enrol and learn more from the course at your own pa





 November 03, 2023
November 03, 2023