Experts define basic interpersonal communication skills as the transfer of a message between two or more people. Therefore, it requires the usage of a broad range of communication tools and mediums in the most simplistic way. Moreover, basic interpersonal communication skills are mostly concerned with bilingual people.
The main objective is to hone and develop English as a second language. And to communicate freely in English. Basic interpersonal communication skills are as important for a business leader as it is for a toddler or a scholar.
Table of Contents
What Are Basic Interpersonal Communication Skills?
Basic interpersonal communication skills is the expanded form of the acronym BICS. The textbook definition of BICS implies conversational skills. The skills required for day to day simplistic communication. You do not need to have a greater set of cognitive skills for conducting interpersonal communication.

BICS is the need for basic language skills for daily social interaction. However, the interaction is in a greater context. Moreover, linguistic experts refer to basic interpersonal communication skills as “playground English”.
Also, they refer to it as context embedded language. That’s because linguistic interactions take place in situational contexts.
Gestures always accompany basic interpersonal communication skills. The gestures make the communication cognitively undemanding. However, it is inadequate to meet the linguistic and analytical demands of a higher academic classroom.
Basic interpersonal communication skills can take place in a classroom setting as well. For instance, when the teacher asks for a student’s help to pass the test papers. The student is already acquainted with the tradition of passing papers from table to table. Thus, this classroom interaction between the teacher and the student was context embedded. Moreover, the communication was interpersonal.
Processing the English language can be cognitively difficult. So, a teacher has to challenge a student in a bilingual class. And the student must learn new ideas, concepts, and the English language all at once.
What Is Cognitive Academic Language Proficiency (CALP)?
Experts refer to a student’s formal academic learning as CALP. CALP means Cognitive Academic Language Proficiency. The CALP is concerned with academic skills. The skills include listening, reading, speaking, and writing on the subject.

When it comes to a student’s academic performance, mastering this language skill is critical. As a student, you must practice language skills important for academic learning. You have to give enough time and be patient with the process.
A student’s ability to obtain the necessary language abilities vary. It could take anywhere from five to seven years. This approach could take up to ten years if a pupil has no prior school experience. Consequently, the time frame extends if the pupil lacks parental assistance.
Moreover, many immigrant parents refuse to learn English. And they converse in their native tongue with their children. So it can have serious implications in the academic and social life of the child. Also, because the child needs to be constantly practising the language. And they need to practice the conversation even in the family environment.
This idea is further complicated. There are various complicated problems that need addressing. For instance, inferring, classifying, comparing, assessing, and synthesising language for content.
Jim Cummins is the creator of this idea. And he has spent a lot of time and effort developing these tactics. The goal is to help ELL children learn more effectively. You can better comprehend the varied strategies to teach ESL and bilingual pupils. But first, you have to be able to distinguish these language learning elements.
A student’s performance in BICS does not always imply that they are ready to go on to academic language study (CALP). So, a teacher must keep that in mind. CALP is a notion that both teachers and students must be patient with.
Elements Of Basic Interpersonal Communication Skills
The basics of interpersonal communication can be broken down into several elements. It helps in better understanding and analysis. The elements include:
The Communicators
Communicators could be two or more people simultaneously. Over the years, many have wrongfully categorised communication as a one-way process. Instead, communicators are the sender and receiver. During communication, the recipient receives the message.

In fact, communication is a two-way process. The process of receiving and giving feedback takes place simultaneously. For instance, while listening to a speech, you could be nodding, smiling. The gestures provide feedback instantaneously.
Message
A simpler definition defines a message as the words said or the information conveyed. But, it also refers to non-verbal signals. It includes facial expressions, tone of voice, gestures, and body language.
Non-verbal behaviour might provide additional information about a message that a person expresses. It can tell more about emotional attitudes. And it may underpin the substance of speech in particular.
Noise
In communication theory, noise has a unique meaning. It refers to anything that distorts the message. It means the received message differs from what the speaker intended. While physical ‘noise,’ such as background noise, can disrupt the conversation, other elements are also called ‘noise.’
The use of jargon, incorrect body language can be termed as distracting noise. Moreover, inattention, apathy, and cultural differences can all be termed ‘noise.’ In other terms, noise can be defined as any distortions or inconsistencies that occur during a communication effort.
Feedback
Feedback is made up of messages that the receiver sends back to the sender. It allows the sender to determine how accurately the message was received.
Furthermore, it lets the sender interpret the receiver’s reaction. Both the unintended and purposeful messages may elicit a response from the receiver.

Direct verbal utterances, such as “Beg your pardon, I don’t understand.” This indicates the recipient is having a hard time comprehending the subject at hand.
Moreover, subtle facial expressions or posture adjustments may indicate to the sender that the recipient is uncomfortable with the message. All these are examples of feedback. Feedback allows the sender to regulate, adjust, or repeat the message to improve communication.
Context
The context in which communication takes place has an impact on it. Contact can take place in a situational context. For instance, in a room, workplace, or possibly outdoors.
In addition, the social context must also be addressed. For example, the duties, responsibilities, and relative status of the participants. Emotional climate and the participants’ expectations will also affect communication.
Channel
The physical means by which a message is transferred from one person to another is referred to as the channel. The channels used in face-to-face interaction are speech and vision. However, during a telephone call, the channel is confined to speech alone.
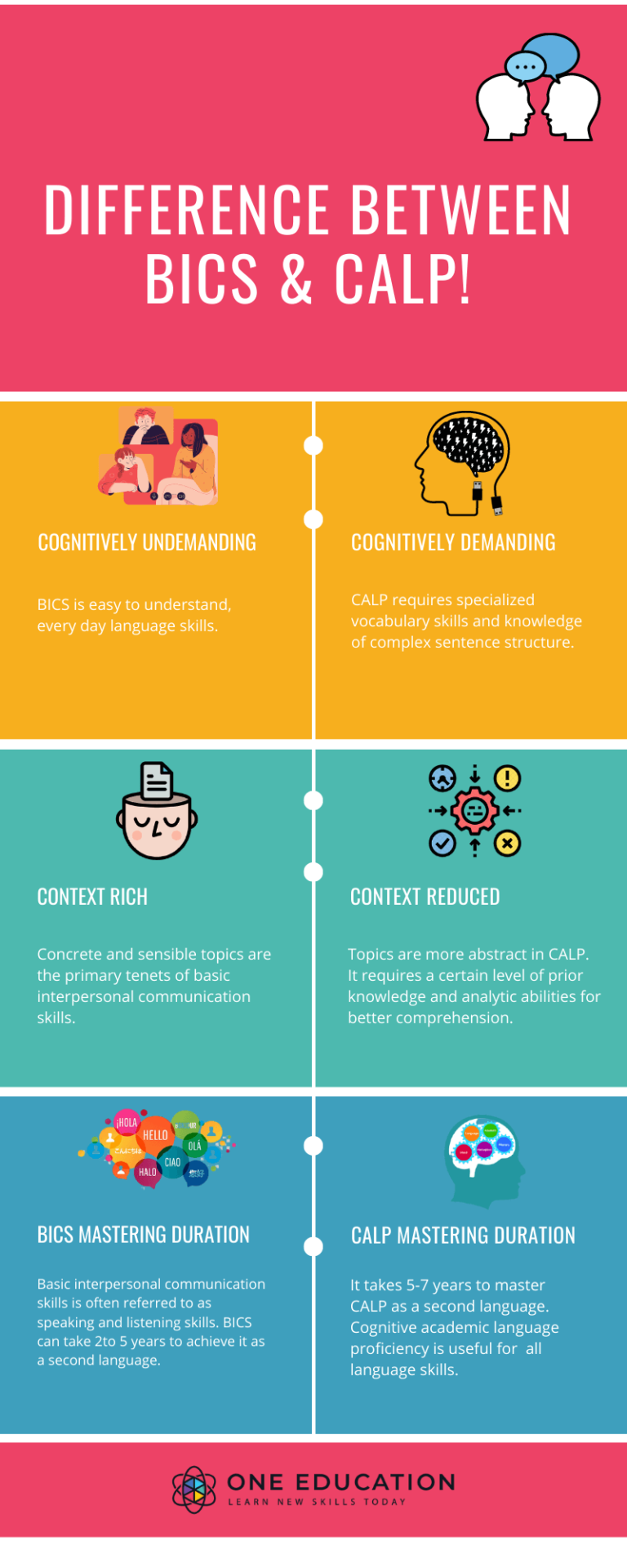
Difference Between Basic Interpersonal Communication Skills & Cognitive Academic Language Proficiency
Basic interpersonal communication skills are context embedded language skills needed for informal interaction. In contrast, cognitive academic language proficiency refers to essential formal academic learning. The context is reduced in CALP, and the language is more abstract.
Role Of Teachers In Developing Basic Interpersonal Communication Skills & Cognitive Academic Language Proficiency
The subtle difference between basic interpersonal communication skills and cognitive academic language proficiency shouldn’t be ignored. However, teachers should not assume students attaining fluency in everyday English can demonstrate the same aptitude in academic language proficiency.
Some progressive approaches can be taken by the teachers to alleviate the struggle ESL students face. As a teacher, you can do the following to help students catch up with their native peers.

Segment Course Module From Beginner To Expert Level
Categorise the tasks in the range from cognitively undemanding to demanding. It will help the students gradually level up instead of cramming in all the information simultaneously.
Be Patient & Emphasize On Keywords

Allow extra time for kids to assimilate new information by slowing down. Make a list of significant words and write them on the board. If they appear to be blank, simplify and restate what you’re saying. Please don’t mention it repetitively, If they didn’t comprehend the first time. If they don’t comprehend the first time, there’s a good probability they won’t understand the second.
Provide One On One Sessions To Protect The Privacy Of Students
Don’t ask the students if they understand the class content in front of the whole class. The majority of overseas students dislike becoming the centre of attention. They will most often just smile and nod, despite not comprehending the matter. They may, in fact, make you believe you are aware of the situation.

Instead, go to them privately while the rest of the group has gone. Moreover, when the class is at work, you can see how they’re tackling the task correctly. You can also put them near your workstation where they would be useful. It’s simple to make eye contact and conduct a quick, quiet conversation with them.
Keep in mind that in many cultures, asking inquiries is frowned upon. Consequently, it is discouraged because it is an indication of ignorance. Therefore, do not be hasty. It is necessary for pupils to approach you as well.
Related: Teaching English as a foreign language
Provide Structured Readings & Take Notes Of Students’ Cultural Perspective
Provide abridged copies of well-known books published in plain English as set texts to help students understand the plot and characters. Keep in mind that themes are elusive. It will be even more so for international students, for immigrant pupils to recognise.

Also, be conscious of cultural differences. We assign weight to things. What we may consider being deplorable, other cultures may seem it as a commendable demonstration of ability and perseverance. For instance, realistic Asians regard materialism as a negative trait. However, many westerners find materialism to be a great force of strength in life.
Supplement Example Essays & Class Content
Provide examples of coursework and other materials. These can be quite useful. However, instruct students that they should not duplicate or memorise any material. And the concept of plagiarism is not an acceptable learning approach.
However, comparing a substandard essay against a good one can often reveal areas that students need to improve. A demonstration is often far more effective than an explanation, which is again laden with language.
Most importantly, keep your students informed about their language learning progress. They might be discouraged by their seeming lack of development. Many people expect to be fluent in their native language within a year. The students and their parents will be completely unaware of how absurd this expectation is.
They may have been top achievers in their home nations. But struggling here in the UK might affect their self-esteem. Hence, you should let students know in advance what the outcome might be the first few years. This will push students to give extra effort. Moreover, knowing that the reason is language barrier instead of intellectual will boost self-confidence.
Related: How to Improve Your Interpersonal Communication Skills
Conclusion
Basic interpersonal communication skills are imperative for personal social, and career development. In a broader aspect, it is almost impossible to function in today’s world if we label interaction in the English language as a foreign matter. To learn how to use Basic interpersonal communication skills, take a look at this Effective Communication Skills course.
Lastly, being bilingual or multilingual, for that matter, pays off really well in the long haul. Hence, put emphasis on linguistics and integrate it into your daily life.
Further resources
- Communication And Interpersonal Skills in Food And Beverage Service
-
The Importance of Effective Communication in Healthcare
- Effective Communication Skills For Social Workers
- 20 Great Jobs to Consider if you have Good Communication Skills
-
Why is Communication Skills of Physicians Important for Patients' Satisfaction?
-
How to Improve Your Interpersonal Communication Skills
- How Do People Develop Cross Cultural Communication Skills?
- Marriage Advice: The 8 Communication Skills of Happy couple
- 10 Essential Communication Skills for Workplace
- 10 Best Assertive Communication Worksheets and Techniques
- How to Tell Someone to Improve Their Communication Skills?
- 20+ Effective Communication Skills (Good for a Resume)






 October 07, 2021
October 07, 2021