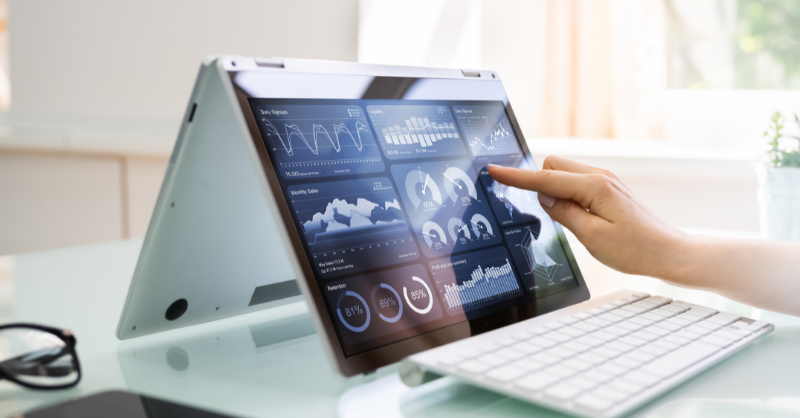
A business dashboard is a summary of key performance indicators (KPIs) or other key data that
show data sets easily. It is important because it collates data from various tools in one place. The
same way a car has many moving parts, your business also has several moving parts that impact
its overall performance.
The purpose of dashboards, thus, is:
1. To offer real-time results by collecting and selecting from the data gathered
2. To create a more comprehensive version of the data by breaking it into smaller bits of visual information that enable you to identify your strengths and areas for improvement.
Dashboards do not only give insight into your company goals but also give a clear view of how to measure the business goals. Change in technology means change in how data is collected. That said, companies generate a lot of data for analysis, but, unfortunately, most of it is not meaningful.
Dashboards, therefore, play a key role to such companies because they provide a solution for analysing the data available. Presenting the data visually in charts and graphs makes it possible to achieve what could not have been done another way.
Microsoft Power BI is a great option for creating dashboards on large sets of business data, and you can make the most of it by taking a training course (Acuity Training is a good option for those based in the UK).
Trainings are another credible resource that you can consider obtaining information from. By using helpful sources, you will gain insights into how to create and share dashboards, among other things of interest. And to help you with the process.
This article will discuss the steps to create a business dashboard.
1. Be Aware Of Your Key Business Objectives
It works best to organise your business objectives in order of priority so that you have high, medium, and low priority categories. With this categorization, you will be able to pick out the key objectives with which you can define the key performance indicators.
2. Be Straightforward
Considering that a dashboard is a single screen with the most important indicators, ensure to display only the essential information. This means that the dashboard should have the most relevant indicators of your business. It should show a representation of the most important data that is related to your current activity. Making use of Excel tabs will help you study the data in depth.
3. Address Problems In Relation To What You Do
Organisations and professional fields are different. Therefore, you should create a dashboard that can accommodate all needs. Organise the data in such a way that there is a screen or a tab for each data query. This will enable the users to get the information they need in order to complete their tasks.
4. Create Action Points
Since the process of building a dashboard constantly evolves, it is important to have it in such a way that it can be revised over time. Revising involves reviewing objectives to ensure that the selection of indicators still serves the users well. For a dashboard to be effective, it should have data that generates actions, such as data that points out areas of concern that should be addressed immediately.
5. Define Performance Indicators
It is expected that each indicator serves the company’s global strategy. Your team will lose focus and end up making the wrong decisions if you have the wrong indicator on the dashboard. Ensure that the indicators are understandable and well modified for everyone who accesses the dashboard. They must also be reliable and can be compared contextually.
6. Use Size And Position To Show Hierarchy
Size and position are elements used to emphasise most important information and to show data that needs to be studied less frequently. The top left corner of the dashboard is considered the most ideal location since that is where your eyes naturally get drawn to first.
7. Have A Mobile Dashboard
While most users prefer using computers to go through reports, others, especially managers and salesmen, could have mobile devices. That said, it is important to make it possible to access a dashboard on mobile devices so that users can interact with data at their fingertips.
8. Group-Related Data
Ensure that the information on your dashboard is logically placed. This means grouping related data next to each other. Grouping related data together makes data easy to find and allows the design of the dashboard to be more attractive.
9. Bring Your Data Closer To Home
As long as your audience understands the data you are presenting, they will receive the message you are trying to pass across better. Therefore, you ought to look for perfect examples that relate to your audience. This is to say that together with giving context, you need to illustrate your data with narratives and experiences.
10. Give Your Numbers Context
Ensure that the numbers you include on your dashboard make sense to the viewers. You can include past data in order to explain the current ones. For instance, you can show 42, 10% to explain that the data is below the threshold required.
11. Make Your Dashboard Easy To Read
It is important to note that data is understood quickly when it can easily be read. Consider that users may not always be familiar with the data format. Thus, it is essential to give them accessible information. For instance, dashboards with so many indicators and graphs will make the user lose interest. To avoid this, present one idea or take advantage of visualization per screen by having many slides in case you have a lot to present.
12. Be Consistent
To make the dashboard easier to read, use the same visualizations and layouts to show the same set of data for multiple things.
13. Have Your Dashboard On One Page
Try as much as you can to have your dashboard on one page. This gives the user a quick look at performance reports. Too much data on multiple pages will make the dashboard lose its resourcefulness and become more of a report.
14. Use The Inverted Pyramid Model
The inverted pyramid model is a kind of model that presents the most important information at the top, then context for all facts in the middle, and further details at the bottom. For instance, a dashboard about growth of sales will have numerical data on revenue and cost at the top. Contextual information, like time frame and new customers, comes in the middle, and then charts and graphs at the bottom. This structure will help the users to understand key facts at a glance. The topic becomes even clearer on further reading.
15. Think About How Best To Plot Your Data
As much as data is used to magnify the truth of what you are saying, it should not have the biggest percentage of your arguments. Contextualizing your data has to be your top priority in order to write a story that revolves around that data. Make your titles and comments easy to read so that the audience is able to follow and anticipate the data being presented.
16. Know What You Want To Achieve
Be clear on what the dashboard will be used for since that will influence its design. Ensure to have a consistent design for the dashboard. This makes it accessible for important data to be viewed daily.
17. Involve Your Team In Creating A Dashboard
This is about discussing with your team members to get their ideas on what they think is important to display on the dashboard. This will enable the team to get the information they need to work on their tasks. It will also help them focus on their goals and avoid being distracted.
18. Think About The Design Of Your Dashboard
There are different ways of displaying a dashboard. It could be on a computer, a TV screen, or a mobile device. For a TV or a computer screen, the measure should be that width is equal to 1920 pixels and height equal to 1080+ pixels. For mobile phones, width is equal to 830 pixels and height is equal to 1920+ pixels. To be able to use both computer and mobile, you should have two different pages on your dashboard.
19. Create Multiple Dashboards
Have separate dashboards for different functions of your business. Similar data could mean different things to people at different levels at a company. Come up with separate dashboards using the same data for each user, then make it possible to access the next levels in case a user would like to.
20. Make Use Of White Space
Ensure that there is some white space between the information to enable the user make sense of the entire dashboard. Too much information in one place may confuse the user.
21. Understand Your Target Audience
You need to know the needs and requirements of your audience in order to package data/information that best suits them. Put yourself in the shoes of your audience and ask yourself whether the reporting tools you are using correspond to the message you want to pass across. Find out if the indicators you are showing are comprehensive enough.
22. Make A Smooth Presentation
Understanding a report usually becomes difficult when the audience is afraid of data and statistics. To address this fear, do your best to guide the audience through the report and make use of data storytelling.
23. Include Colour Coding
Use different colours to show trends like increase and decrease. This helps the user get an overall picture. Invest in time to learn how to assign and use colour.
24. Use Both Tables And Graphs
Graphs and tables are for different purposes. Use graphs to help the users compare numbers broadly and tables to monitor or get specific numbers.
25. Segment Data
See to it that you have the most crucial data at the top and middle sections of the dashboard. This is so that you have the most sought-after information easily available (at the top of the dashboard).
26. Use Emojis To Label Your Dashboard
It may be difficult to organise your work and see all tabs (in case you are using Google sheets). Instead, use emoji-based labels, like target emojis, for goals.
27. Follow Data Research-Based Practices
This is good for effective data communication. The standards that come with research-based practices make it easier for the user to understand so that they do not need to have an expert next to them to take them through.
28. Scrutinise Data And Its Usability
Be sure to improve the relationship that exists between data and its usability. You could liken a dashboard to a funnel where quite a lot of information goes to the top, and then it is refined to what the user may need. Remember also that the technical abilities of the users are different. Thus, simplifying them whenever possible will go a long way.
29. Avoid Perfectionism
It is important to note that no dashboard will provide possible answers in a single view to an evolving business. Trying to achieve this will only end up in tangled choices, alternatives, and options for the user. Of utmost importance is to know your users, to keep your data uncluttered, to have a simple design, and to tell a story.
30. Keep Updating Your Dashboard
Get feedback from your team as often as possible. Find out what they look at most, what they find useful and why. Find out too if there is anything missing that they would find useful and if the dashboard has changed anything about how the team works.
To Wrap Up
Dashboards are created for a myriad of reasons, ranging from monitoring performance to flagging issues that need immediate attention. In this step-by-step discussion of how to create a business dashboard, there are key elements that stand out. They include design of the dashboard, which determines whether it will meet its objectives and target audience, and the people who should use the dashboard to make decisions and act on them accordingly.
It is encouraging to know that you do not need any expertise to build a dashboard. As long as your overall objective is to communicate your data and key goals clearly, the above steps are a good guide to follow.
Recent posts
- Why is Child Development so Important in Early Years
- Line Management: How to be a Good Line Manager?
- How Long Should a Health Sector Career Take?
- The Importance of BSL in Everyday Life
- Why Corporate eLearning is Essential for Organisational Training
- Take your Business Expertise to the next level: Get your MBA
- Read to Lead: Books That Cultivate Effective Leadership Skills
- Crafting an Effective Home Schooling Curriculum: A Comprehensive Guide
- Learn How to Write a Term Paper | From Start to Finish
- Student Entrepreneurship: Creating and Selling Custom T-Shirts as a Learning Experience






 July 14, 2021
July 14, 2021








